ECONYL is an innovative, regenerated nylon fiber made entirely from waste materials, including discarded fishing nets, old carpets, and industrial plastic scraps. Developed by the Italian company Aquafil in 2011, ECONYL has revolutionized the way synthetic fibers contribute to a circular and more sustainable textile economy. Identical in performance and quality to virgin nylon, it combines durability and flexibility with a significantly lower environmental footprint, making it a leading material in sustainable fashion, swimwear, and activewear.
The creation of ECONYL begins with the collection of nylon waste from around the world. This waste includes abandoned “ghost nets” recovered from the oceans, pre-consumer waste such as factory offcuts, and post-consumer waste, including used carpets and plastic components. These materials are sorted, cleaned, and shredded into smaller pieces before entering a proprietary regeneration process that restores the nylon polymers to their original purity and integrity. Unlike recycling, which typically degrades material quality, ECONYL utilizes a chemical depolymerization process that breaks down nylon into its raw monomers and rebuilds it into brand-new nylon 6 polymer.

This process yields a fiber that is chemically identical to virgin nylon 6, allowing it to be used in the same applications without any loss in strength, elasticity, or durability. However, its environmental impact is substantially lower. Producing ECONYL reduces global warming potential by up to 90% compared to conventional nylon and avoids the use of new petroleum resources. After its life cycle ends, ECONYL products can be broken down and regenerated, creating a closed-loop system that supports circular design.
The properties of ECONYL mirror those of standard nylon: it is lightweight, strong, abrasion-resistant, and highly elastic. These qualities make it ideal for performance-oriented textiles such as swimwear, leggings, outerwear, and sports gear, as well as carpets and upholstery. Its smooth texture and stretch recovery make it especially popular among fashion brands seeking to combine comfort with sustainability. ECONYL also resists mold, UV damage, and chlorine, offering long-lasting quality that enhances product lifespan.
Since its launch, ECONYL has become a favorite among both luxury and sustainable fashion labels. Brands such as Stella McCartney, Prada, Adidas, and Gucci utilize ECONYL in a range of products, including swimwear, handbags, sneakers, and technical outerwear. The material’s transparent supply chain and closed-loop production model appeal to designers aiming to minimize waste while maintaining high-performance standards. Additionally, its story of transforming ocean waste into luxury fashion resonates strongly with environmentally conscious consumers.
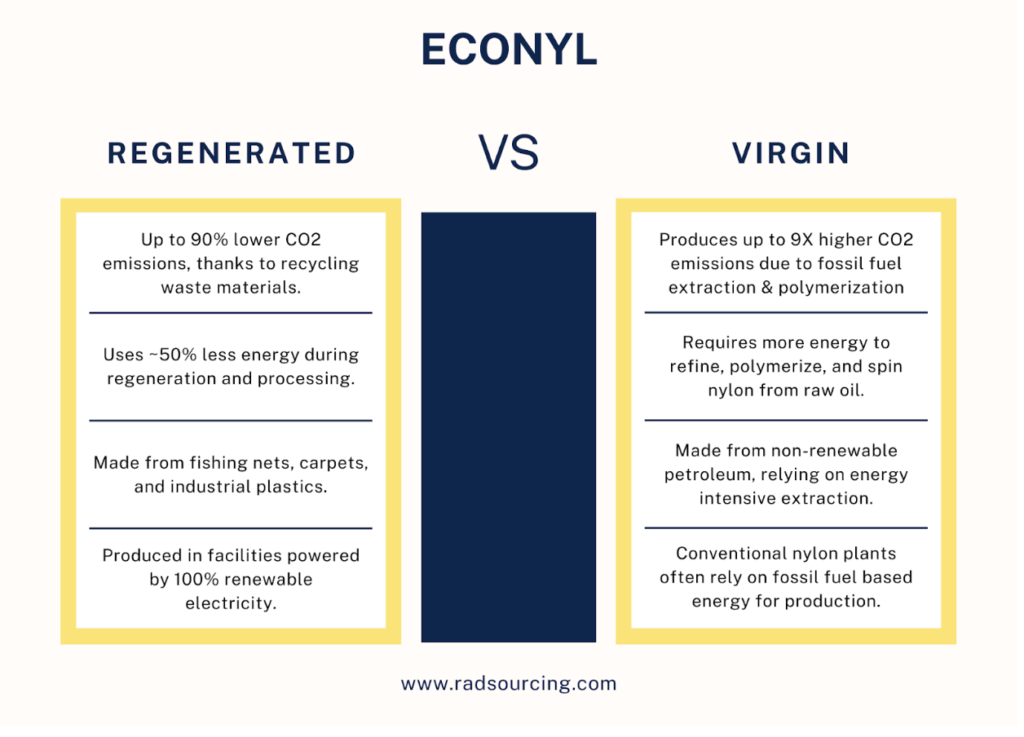
From a sustainability perspective, ECONYL represents a significant advancement in synthetic textile innovation. Traditional nylon is derived from crude oil and requires intensive energy to produce, emitting large quantities of greenhouse gases. ECONYL, by contrast, uses waste as a raw material and recycles it infinitely without loss of quality, drastically reducing environmental and resource impacts. Its regeneration system recovers and reuses all by-products, ensuring nearly zero waste during production. However, like all synthetics, ECONYL garments can still shed microfibers during washing, so proper care and filtration remain important for minimizing ocean pollution.
Globally, ECONYL is produced primarily in Italy at Aquafil’s state-of-the-art regeneration plant in Arco, Trentino, with supporting waste recovery networks across North America, Asia, and Europe. The company collaborates with environmental initiatives such as Healthy Seas, which recovers abandoned fishing nets, and partners with manufacturers to create closed-loop supply systems. This integrated approach ensures traceability and ethical sourcing throughout production.
ECONYL embodies the future of sustainable textiles by proving that high performance and environmental responsibility can coexist. Through cutting-edge regeneration technology, it transforms discarded materials into a premium, infinitely recyclable fiber that reduces waste and dependency on fossil fuels. As the textile industry moves toward circularity, ECONYL stands as a model of how innovation can restore, rather than exploit, resources, transforming pollution into a potential resource.
